Education
A Turning Point in AI: OpenAI’s “AI Progress and Recommendations”

- Share
- Tweet /data/web/virtuals/375883/virtual/www/domains/spaisee.com/wp-content/plugins/mvp-social-buttons/mvp-social-buttons.php on line 63
https://spaisee.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/sam_altman-1000x600.png&description=A Turning Point in AI: OpenAI’s “AI Progress and Recommendations”', 'pinterestShare', 'width=750,height=350'); return false;" title="Pin This Post">
Capabilities Advancing, but the World Stays the Same
In a post shared recently by Sam Altman, OpenAI laid out a new framework reflecting just how far artificial intelligence has come — and how far the company believes we have yet to go. The essay begins with the recognition that AI systems today are performing at levels unimaginable only a few years ago: they’re solving problems humans once thought required deep expertise, and doing so at dramatically falling cost. At the same time, OpenAI warns that the gap between what AI is capable of and what society is actually experiencing remains vast.
OpenAI describes recent AI progress as more than incremental. Tasks that once required hours of human effort can now be done by machines in minutes. Costs of achieving a given level of “intelligence” from AI models are plummeting — OpenAI estimates a roughly forty-fold annual decline in cost for equivalent capability. Yet while the technology has advanced rapidly, everyday life for most people remains largely unchanged. The company argues that this reflects both the inertia of existing systems and the challenge of weaving advanced tools into the fabric of society.
Looking Ahead: What’s Next and What to Expect
OpenAI forecasts that by 2026 AI systems will be capable of “very small discoveries” — innovations that push beyond merely making human work more efficient. By 2028 and beyond, the company believes we are likely to see systems that can make even more significant discoveries — though it acknowledges the uncertainties inherent in such predictions. The post also underscores that the future of AI is not just about smarter algorithms, but about shaped social, economic and institutional responses.
A Framework for Responsible Progress
The document outlines three major pillars that OpenAI deems essential for navigating the AI transition responsibly. First, labs working at the frontier must establish shared standards, disclose safety research, and coordinate to avoid destructive “arms-race” dynamics. In OpenAI’s view, this is akin to how building codes and fire standards emerged in prior eras.
Second, there must be public oversight and accountability aligned with the capabilities of the technology — meaning that regulations and institutional frameworks must evolve in concert with rising AI power. OpenAI presents two scenarios: one in which AI evolves in a “normal” mode and traditional regulatory tools suffice, the other in which self-improving or super-intelligent systems behave in novel ways and demand new approaches.
Third, the concept of an “AI resilience ecosystem” is introduced — a system of infrastructure, monitoring, response teams and tools, analogous to the cybersecurity ecosystem developed around the internet. OpenAI believes such resilience will be crucial regardless of how fast or slow AI evolves.
Societal Impact and Individual Empowerment
Underlying the vision is the belief that AI should not merely make things cheaper or faster, but broaden access and improve lives. OpenAI expects AI to play major roles in fields like healthcare diagnostics, materials science, climate modeling and personalized education — and aims for advanced AI tools to become as ubiquitous as electricity, clean water or connectivity. However, the transition will be uneven and may strain the socioeconomic contract: jobs will change, institutions may be tested, and we may face hard trade-offs in distribution of benefit.
Why It Matters
This statement represents a turning point — not just for OpenAI, but for the AI ecosystem broadly. It signals that leading voices are shifting from what can AI do to how should AI be governed, deployed and embedded in society. For investors, policy-makers and technologists alike, the message is clear: the existence of powerful tools is no longer the question. The real question is how to capture their upside while preventing cascading risk.
In short, OpenAI is saying: yes, AI is now extremely capable and moving fast. But the institutions, policies and social frameworks around it are still catching up. The coming years are not just about brighter tools — they’re about smarter integration. And for anyone watching the next phase of generative AI, this document offers a foundational lens.
AI Model
How to Get Factual Accuracy from AI — And Stop It from “Hallucinating”

Everyone wants an AI that tells the truth. But the reality is — not all AI outputs are created equal. Whether you’re using ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini, the precision of your answers depends far more on how you ask than what you ask. After months of testing, here’s a simple “six-level scale” that shows what separates a mediocre chatbot from a research-grade reasoning engine.
Level 1 — The Basic Chat
The weakest results come from doing the simplest thing: just asking.
By default, ChatGPT uses its Instant or fast-response mode — quick, but not very precise. It generates plausible text rather than verified facts. Great for brainstorming, terrible for truth.
Level 2 — The Role-Play Upgrade
Results improve dramatically if you use the “role play” trick. Start your prompt with something like:
“You are an expert in… and a Harvard professor…”
Studies confirm this framing effect boosts factual recall and reasoning accuracy. You’re not changing the model’s knowledge — just focusing its reasoning style and tone.
Level 3 — Connect to the Internet
Want better accuracy? Turn on web access.
Without it, AI relies on training data that might be months (or years) old.
With browsing enabled, it can pull current information and cross-check claims. This simple switch often cuts hallucination rates in half.
Level 4 — Use a Reasoning Model
This is where things get serious.
ChatGPT’s Thinking or Reasoning mode takes longer to respond, but its answers rival graduate-level logic. These models don’t just autocomplete text — they reason step by step before producing a response. Expect slower replies but vastly better reliability.
Level 5 — The Power Combo
For most advanced users, this is the sweet spot:
combine role play (2) + web access (3) + reasoning mode (4).
This stack produces nuanced, sourced, and deeply logical answers — what most people call “AI that finally makes sense.”
Level 6 — Deep Research Mode
This is the top tier.
Activate agent-based deep research, and the AI doesn’t just answer — it works. For 20–30 minutes, it collects, verifies, and synthesizes information into a report that can run 10–15 pages, complete with citations.
It’s the closest thing to a true digital researcher available today.
Is It Perfect?
Still no — and maybe never will be.
If Level 1 feels like getting an answer from a student doing their best guess, then Level 4 behaves like a well-trained expert, and Level 6 performs like a full research team verifying every claim. Each step adds rigor, depth, and fewer mistakes — at the cost of more time.
The Real Takeaway
When people say “AI is dumb,” they’re usually stuck at Level 1.
Use the higher-order modes — especially Levels 5 and 6 — and you’ll see something different: an AI that reasons, cites, and argues with near-academic depth.
If truth matters, don’t just ask AI — teach it how to think.
AI Model
81% Wrong: How AI Chatbots Are Rewriting the News With Confident Lies
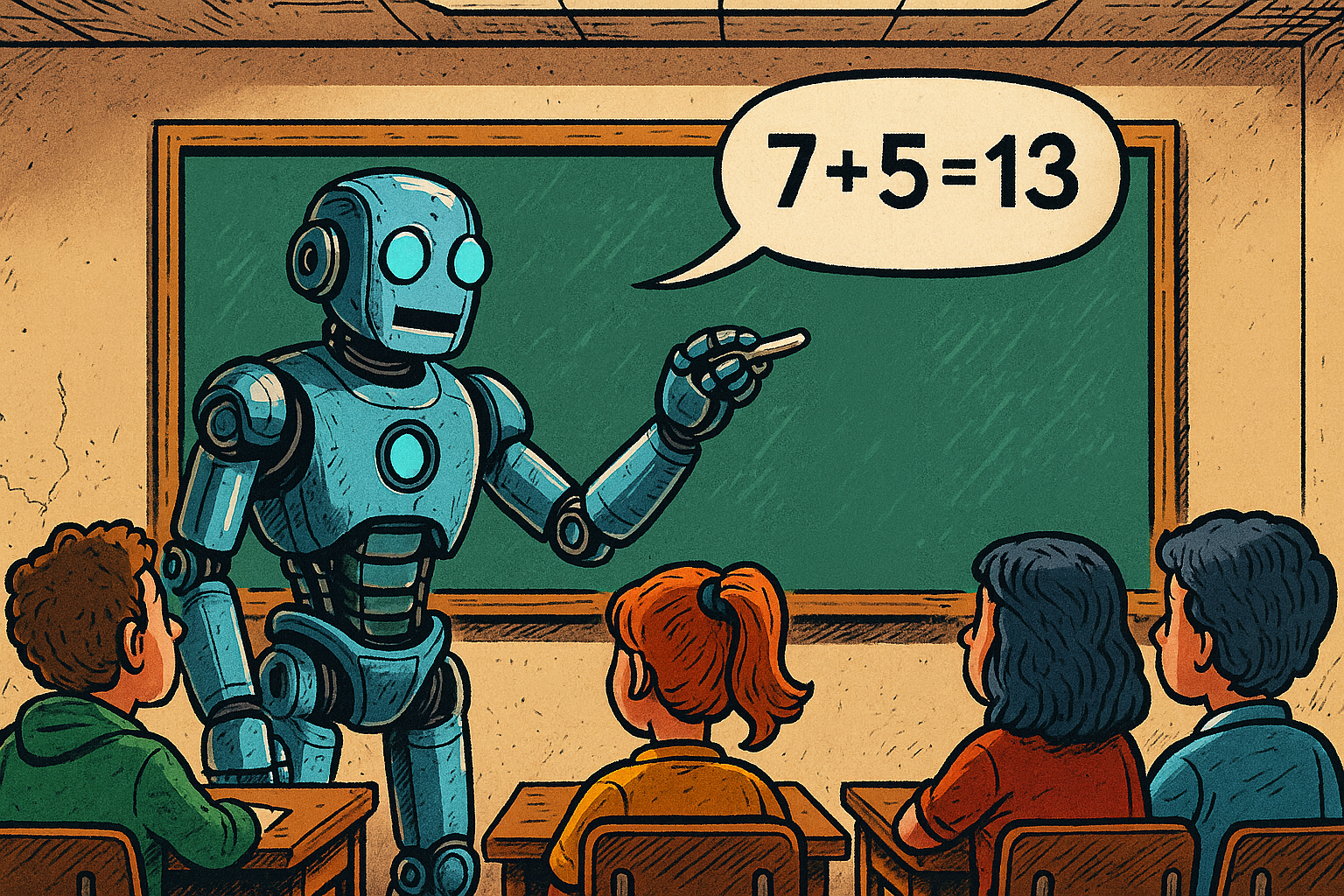
In 2025, millions rely on AI chatbots for breaking news and current affairs. Yet new independent research shows these tools frequently distort the facts. A European Broadcasting Union (EBU) and BBC–supported study found that 45% of AI-generated news answers contained significant errors, and 81% had at least one factual or contextual mistake. Google’s Gemini performed the worst, with sourcing errors in roughly 72% of its responses. The finding underscores a growing concern: the more fluent these systems become, the harder it is to spot when they’re wrong.
Hallucination by Design
The errors aren’t random; they stem from how language models are built. Chatbots don’t “know” facts—they generate text statistically consistent with their training data. When data is missing or ambiguous, they hallucinate—creating confident but unverified information.
Researchers from Reuters, the Guardian, and academic labs note that models optimized for plausibility will always risk misleading users when asked about evolving or factual topics.
This pattern isn’t new. In healthcare tests, large models fabricated medical citations from real journals, while political misinformation studies show chatbots can repeat seeded propaganda from online data.
Why Chatbots “Lie”
AI systems don’t lie intentionally. They lack intent. But their architecture guarantees output that looks right even when it isn’t. Major causes include:
- Ungrounded generation: Most models generate text from patterns rather than verified data.
- Outdated or biased training sets: Many systems draw from pre-2024 web archives.
- Optimization for fluency over accuracy: Smooth answers rank higher than hesitant ones.
- Data poisoning: Malicious actors can seed misleading information into web sources used for training.
As one AI researcher summarized: “They don’t lie like people do—they just don’t know when they’re wrong.”
Real-World Consequences
- Public trust erosion: Users exposed to polished but false summaries begin doubting all media, not just the AI.
- Amplified misinformation: Wrong answers are often screenshot, shared, and repeated without correction.
- Sector-specific risks: In medicine, law, or finance, fabricated details can cause real-world damage. Legal cases have already cited AI-invented precedents.
- Manipulation threat: Adversarial groups can fine-tune open models to deliver targeted disinformation at scale.
How Big Is the Problem?
While accuracy metrics are worrying, impact on audiences remains under study. Some researchers argue the fears are overstated—many users still cross-check facts. Yet the speed and confidence of AI answers make misinformation harder to detect. In social feeds, the distinction between AI-generated summaries and verified reporting often vanishes within minutes.
What Should Change
- Transparency: Developers should disclose when responses draw from AI rather than direct source retrieval.
- Grounding & citations: Chatbots need verified databases and timestamped links, not “estimated” facts.
- User literacy: Treat AI summaries like unverified tips—always confirm with original outlets.
- Regulation: Oversight may be necessary to prevent automated systems from impersonating legitimate news.
The Bottom Line
The 81% error rate is not an isolated glitch—it’s a structural outcome of how generative AI works today. Chatbots are optimized for fluency, not truth. Until grounding and retrieval improve, AI remains a capable assistant but an unreliable journalist.
For now, think of your chatbot as a junior reporter with infinite confidence and no editor.
Education
Fluent in Code: Navigating the New World of AI-Powered Language Learning

Learning a foreign language has always required commitment — hours of practice, expensive classes, and exposure to native speakers. But now, a new companion has entered the scene: artificial intelligence. With AI models like ChatGPT, tools powered by Grok’s Ani, and a wave of emerging apps, it’s never been easier—or cheaper—to start your language journey. But can these digital tutors really deliver fluency? Let’s dive into the possibilities, pitfalls, and the best free or low-cost AI tools available right now.
The AI Advantage: Why More People Are Skipping the Classroom
AI offers a compelling pitch for anyone intimidated by traditional language learning routes. The tools are available 24/7, often free or inexpensive, and adapt instantly to your level and interests. Here’s why it’s catching on:
- Cost-effective: Many general-purpose AI models like ChatGPT offer free tiers or require only a basic subscription, making them far cheaper than classes or tutors.
- Always-on access: Whether it’s midnight or your lunch break, AI doesn’t sleep. You can practice anytime, anywhere.
- Custom feedback: AI can correct your grammar, suggest better word choices, and even roleplay everyday scenarios in your target language.
- Zero judgment: Learners often feel anxious about speaking with humans. AI offers a pressure-free way to make mistakes and learn from them.
In essence, AI gives you a patient, tireless, and responsive partner. But it’s not a silver bullet.
The Drawbacks: What AI Still Can’t Do
While AI language learning tools are powerful, they’re not flawless. Here’s where they fall short:
- Cultural nuance is limited: AI may know grammar, but it often misses idioms, tone, and the social subtleties of real communication.
- Risk of errors: AI can sometimes provide inaccurate or unidiomatic translations or explanations. Without a human teacher, you might not know what’s off.
- Speech limitations: Even with voice-enabled tools, AI pronunciation might not match native speech exactly — and it can struggle to understand heavily accented input.
- No real-world exposure: AI can’t replicate the experience of talking to a real person in a café, on the street, or in a business meeting.
- Motivation still matters: AI might be engaging, but it won’t push you to keep going. You’re still the one who has to show up every day.
The verdict? AI is a fantastic assistant but works best as part of a broader learning strategy that includes immersion, real interaction, and diverse resources.
Mapping the AI Language Learning Landscape
So, what are your options if you want to get started? Here’s an overview of the most popular and accessible ways people are using AI to learn languages — with a focus on free or low-cost tools.
1. ChatGPT and General AI Chatbots
One of the most flexible approaches is using a general-purpose model like ChatGPT (from OpenAI) or Claude (from Anthropic) as your language partner. Just prompt it to:
- “Speak only in French and help me practice everyday conversation.”
- “Correct my Spanish paragraph and explain the grammar mistakes.”
- “Teach me five useful idioms in Italian.”
Many learners use ChatGPT’s voice feature to practice listening and speaking, even roleplaying restaurant scenarios or travel situations. It’s like having a personal tutor who never runs out of patience.
2. Grok’s Ani: The Friendly AI Tutor
If you’re part of the Grok AI ecosystem, you may have access to Ani, a conversational AI designed to help users learn languages in a more interactive and emotionally intelligent way. Ani aims to go beyond correction—it encourages, adapts, and even gives personality to your learning partner. Users report that the emotional tone and feedback from Ani helps build confidence, especially in early stages of learning.
3. Voice-Based AI Tools
For those who want to speak and be heard, apps like Gliglish and TalkPal let you practice conversations using your voice. These tools simulate real-life dialogues and provide real-time feedback. They often use GPT-style models on the backend, with some offering limited free daily usage.
- Gliglish: Offers free speaking practice and realistic conversation scenarios.
- TalkPal: Lets you converse by text or voice, with personalized feedback.
These are great for practicing pronunciation and spontaneous response — key skills for fluency.
4. AI-Powered Apps with Freemium Models
Several newer apps integrate LLMs like GPT to offer personalized lessons, dialogues, or speaking drills:
- Speak: Uses OpenAI’s tech to simulate natural conversations and offers corrections.
- Loora AI and LangAI: Focus on business or casual dialogue training using AI chats.
While many of these are paid, they typically offer free trials or limited daily use, enough for a solid daily practice session without a subscription.
5. DIY AI Setups and Open Source Tools
Tech-savvy learners are also building their own setups using tools like OpenAI’s Whisper (for speech recognition) combined with GPT for dialogue generation. Guides exist for setting up roleplay bots, combining voice input and AI-generated responses for a truly custom tutor experience.
For written language learning, tools like Tatoeba (a multilingual sentence database) or LanguageTool (an open-source grammar checker) can be used alongside AI to get example sentences or polish writing.
What People Are Actually Using
Among language learners, the most common practice seems to be leveraging ChatGPT or similar LLMs to:
- Practice writing and get corrections
- Simulate conversation scenarios
- Translate and explain phrases
- Build vocabulary with flashcards or custom quizzes
Many learners supplement this with speech-based apps or tools like Gliglish for pronunciation and conversation. Community feedback on Reddit and language forums consistently highlights the flexibility and personalization AI provides as the main draw.
Final Thoughts: Should You Learn a Language with AI?
If you’re considering learning a new language, AI offers an incredibly accessible, customizable, and low-pressure entry point. You can use it to build a habit, sharpen your skills, and explore a language before committing to more intensive study.
But remember: AI is a tool, not a replacement for the real-world experience. Use it to complement human interaction, cultural immersion, and diverse materials. The best results come when you combine AI’s strengths—endless practice, instant feedback, low cost—with your own curiosity and consistency.
So go ahead — say “bonjour” to your new AI tutor.
-

 AI Model6 months ago
AI Model6 months agoTutorial: How to Enable and Use ChatGPT’s New Agent Functionality and Create Reusable Prompts
-

 AI Model4 months ago
AI Model4 months agoHow to Use Sora 2: The Complete Guide to Text‑to‑Video Magic
-

 AI Model5 months ago
AI Model5 months agoTutorial: Mastering Painting Images with Grok Imagine
-

 AI Model7 months ago
AI Model7 months agoComplete Guide to AI Image Generation Using DALL·E 3
-
 AI Model7 months ago
AI Model7 months agoMastering Visual Storytelling with DALL·E 3: A Professional Guide to Advanced Image Generation
-

 Tutorial4 months ago
Tutorial4 months agoFrom Assistant to Agent: How to Use ChatGPT Agent Mode, Step by Step
-

 AI Model9 months ago
AI Model9 months agoGrok: DeepSearch vs. Think Mode – When to Use Each
-

 News4 months ago
News4 months agoOpenAI’s Bold Bet: A TikTok‑Style App with Sora 2 at Its Core











